Adding restrictions to the 2D Model
Last updated
Was this helpful?
Last updated
Was this helpful?
It is possible to add restrictions by to prepare for students.
There are three types of restrictions:
Time restrictions. For example, a time limit to complete a task or a specific action in a specific time frame.
Spatial. For example, adding regions ("Start", "Finish") or prohibiting/forcing a robot, its sensor, or some moving object to be at a certain time in a certain place.
Device restrictions. For example, a limitation on the set of sensors or on the behavior of devices.
The main tagwhich contains all the restrictions is used to describe them. Used as a container. Restrictions are described inside the tag, each inner tag must be one of four:
Tag
Description
Time limit.
A constraint with an arbitrary condition in violation of which a specified error will be generated.
The main tool for setting dynamic constraints. Used as a container.
An unconditional event that runs before the program starts executing.
The main tag containing all restrictions. Used as a container.
Time limit. Mandatory.
Attribute
Description
value="value"
Timeout in milliseconds after which the execution will be terminated and the "Time limit exceeded" error will be displayed.
A constraint with an arbitrary condition. If the condition is violated a specified error message will be displayed. Can be used as a container. Has one child tag: <conditions>...</conditions>.
Attribute
Description
checkOnce="true"
Boolean attribute. If the value is true, then the restriction will be checked once at program startup. Is useful for one-time checks such as sensor layout etc.
failMessage="Error!"
An error message will be displayed when a restriction is violated.
The main tool for setting dynamic constraints. Used as a container.
Attribute
Description
settedUpInitially="true"
An attribute that allows you to indicate whether the event is set up at the start of the program. The event can be set up or dropped. In the setup state, the event pulls its trigger if its condition is met, otherwise it's just ignored by the system.
The default value is false.
id="finish checker"
Events unique ID. The event can be referred by id from others. Optional.
dropsOnFire = "true"
A boolean attribute that indicates whether the event should continue to be set up after it is triggered or not. Optional. The default value is true.
Unconditional event executing before the program starts.
Example:
The condition being checked is described inside this tag.
Example:
Used to create compound conditions. The logical bond is the mandatory attribute. The bond may be and or or. Negation is specified by the <not> tag without attributes. Other <conditions> elements may also appear among subexpressions.
Attribute
Description
glue="and"
Logical bond.
Atomic condition is one of the following elements:
Tag
Description
Value comparison operations.
Sets spatial constraints.
Checks whether an event is set up or not.
Sets the time in ms after which the specified condition is considered true.
Equals. The functional symbols value comparison operation. Can be used as a container.
Not equal. The functional symbols value comparison operation. Can be used as a container.
Greater. The functional symbols value comparison operation. Can be used as a container.
Less. The functional symbols value comparison operation. Can be used as a container.
Sets spatial constraints.
Attribute
Description
objectId="id"
Object ID.
regionId="id"
Region ID.
Checks whether the event set up or not.
Attribute
Description
id="event1"
The ID of the event is checked
The "check event" event conditions check that the other "Try move" event is set up and the "Go back" event is dropped. If both of them return "true" after the check the program successfully ends.
A predicate that starts to return "true" when the specified time has passed since the moment when this event was set, and up to that moment it returns "false".
Attribute
Description
timeout="1000"
The time interval after which this predicate will become true. Mandatory. The value must be a non-negative integer.
forceDropOnTimeout="true"
A Boolean attribute that allows you to drop the event that has this timer in a condition.
If set to true, the event will be dropped even if there are other active timers and unmet conditions. Optional. The default value is true.
Let's look at using <timer/> with different forceDropOnTimeout attribute values.
The "check region" event checks time and spatial limits. The first condition (timer) becomes true after 1000ms. Its value doesn't change after that. The second one (inside) checks that the robot is inside the "start_zone" region. When both conditions will be met simultaneously the program will end successfully.
1. Since the forceDropOnTimeout attribute is "false", the event will be still set up after a specified timeframe and wait for the second condition to be met.
2. Since the forceDropOnTimeout attribute is "true", the event will be dropped after the specified timeframe despite the presence of a second condition. Therefore, if the robot is not in the required region right after 1000 ms, then the success message will not be displayed even if the robot will be there after some time.
Variable or operation
Description
Integer, fractional, string, and boolean constants.
Variable value.
Get the object state.
Get the meta-type of the object with the specified identifier.
Unary arithmetic functions that have exactly one child, which must be an integer value.
Binary arithmetic functions that have exactly two child elements, each of them must be an integer.
Setting a constant.
Attribute
Description
value="0″
Constant value.
Variable value.
It is possible to take the property of any variable using a dot. For example, "rect.width" will return the width of the rectangle stored in "rect".
Attribute
Description
name="my_value"
Variable name
Get the object state.
Attribute
Description
object="robot1.display.labels.size"
Object ID
Get the objects with specified ID meta-type. For example, the type of the wall object with id=777 will be wall.
Most often, this element will be needed to check the type of connected sensors and motors.
Attribute
Description
objectId="id"
Objects unique ID.
Unary arithmetic operations for changing the sign and taking the modulus of a number.
Sum and difference of values. Minimum and maximum value.
Tag
Description
An action or a group of actions that will be performed one or many times after the event condition is met.
Display an error message. Finish checking the task.
Display success message, finish the check.
Set the variable value.
Setting or dropping the event.
An action or a group of actions that will be performed one or many times after the event condition is met.
Display an error message. Finish checking the task.
Attribute
Description
message="Wrong answer!"
Error message text
The task is successfully done.
Attribute
Description
deffered="false"
Optional. The default value is "false". If set to "true" the trigger won't stop the program, I. e. the checker will wait until the program finishes and either reports the success if there were no errors, or otherwise, it will finish with an error. In other words, you won't get the error "The program has finished, but the task is not completed": the program will either terminate successfully or with a meaningful error like "Time limit exceeded".
Set the variable value.
Attribute
Description
name="my_value"
Variable name
Setting up or dropping an event.
Attribute
Description
id="finish checker"
The ID of the event.
Name
Description
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::RangeSensor
Distance sensor
trik::robotModel::twoD::parts::TwoDLightSensor
Light sensor
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::TouchSensor
Touch sensor
trik::robotModel::twoD::parts::LineSensor
Line sensor
Name
Description
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::RangeSensor
Distance sensor
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::LightSensor
Light sensor
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::TouchSensor
Touch sensor
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::ColorSensorRed
Color sensor (red)
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::ColorSensorGreen
Color sensor (green)
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::ColorSensorBlue
Color sensor (blue)
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::ColorSensorPassive
Color sensor (passive)
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::ColorSensorFull
Color sensor EVX/NXT (color)
twoDModel::robotModel::parts::ColorSensorAmbient
Color sensor EV3 (ambient)
ev3::robotModel::twoD::parts::GyroscopeSensor
Gyroscope
ev3::robotModel::twoD::parts::GyroscopeSensor
Compass
Property
Description
robot1.rotation
A current robot's rotation angle
robot1.x and robot1.y
Robots coordinate
robot1.led.color
LED color
robot1.marker.isDown
Checks if the robot has a marker and it draws a line on the field. Returns "true" or "false".
robot1.shell.lastPhrase
Get the last robots phrase.
Property
Description
robot1.display.sadSmiles
Checks if there is a sad smile on the controller display. Returns "true" or "false".
robot1.display.smiles
Checks if there is a happy smile on the controller display. Returns "true" or "false".
robot1.display.labels.first.text
Message (label) text that was displayed first.
robot1.display.labels.last.text
Message (label) text that was displayed last.
robot1.display.labels.size
Get the displayed label number.
Checking that the word “message” was displayed on the controller screen. The case is important.
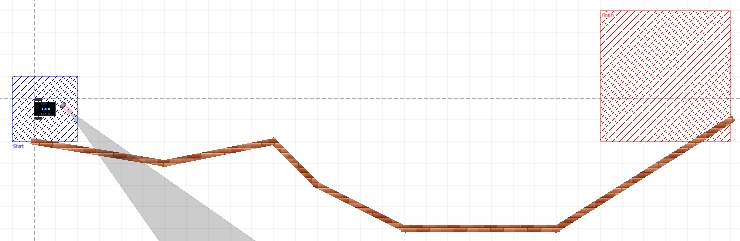
You need to start in the blue square then drive along the wall to the red one using the IR distance sensor.
An event is just a pair (, ).
Now lets talk about the conditions in the and elements. Conditions are set using the tag if only one of the is tested, or the tag if a compound condition is tested.
, , ,